Table of Contents
The opioid crisis represents a major public health emergency, having claimed countless lives through addiction and overdose. The number of drug overdose deaths increased by more than 16% from 2020 to 2021.
Over 75% of the nearly 107,000 drug overdose deaths in 2021 involved an opioid.[1] One estimate reported that with the wide range of costs considered, the costs of the opioid crisis in the U.S. alone go up to a staggering amount of more than $1 trillion a year [2].
Opioids like fentanyl have recently been most notorious for their lethal potency, but a new class of synthetic opioid street drugs, known as Nitazenes, is emerging as an even greater threat. This article helps parents and guardians (and teens) understand what they are, their dangers, and strategies for helping teens avoid a tragic fate.
Nitazenes Hit the Streets
Nitazenes, developed initially for pharmaceutical purposes but never approved for medical use, are surfacing on the streets, posing a significant risk due to their extreme potency—reportedly in some cases, up to many times stronger than fentanyl.
Nitazenes are a class of synthetic opioids that contains more than 20 unique compounds, including isotonitazene, which was first identified in 2019 and is known on the streets as “ISO” and “Tony”. Even though nitazenes have been identified in the illicit recreational drug supply, few parents know what they are and few clinicians are aware of them or their implications for emergency medicine.
This alarming development underscores the urgency of guarding teens against these substances, as their increased strength amplifies the risk of overdose and death.

What Are Nitazenes?
Nitazenes are a group of synthetic opioids, originally synthesized in the 1950s and 1960s as part of pharmaceutical research, but were never approved for medical use. These compounds were initially investigated for their analgesic properties, with the hope that they could serve as effective pain relievers.
However, due to their potent effects and the potential for abuse, development was halted, and they remained largely obscure in medical science—until underground chemists discovered them in the historical 1950s pharmacological literature.
The chemical structure of Nitazenes is characterized by a nitrobenzimidazole core, which differentiates them from other opioids that typically contain a morphine backbone or its synthetic equivalents. This unique structure contributes to their high potency and affinity for the mu-opioid receptors in the brain, the primary sites responsible for opioids’ pain-relieving and euphoric effects.
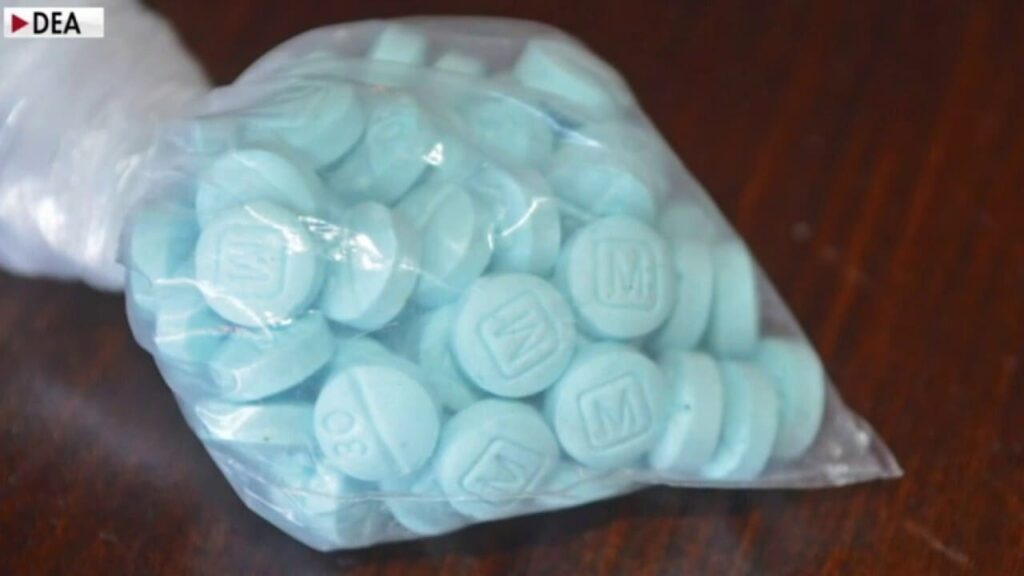
The rise of Nitazenes in recent years marks a concerning evolution in the opioid crisis. These substances have begun to surface more frequently on the drug scene as “designer drugs”, often found in combination with other drugs or misrepresented as less potent opioids. These nitazene designer drugs are currently considered esoteric drugs that evade conventional toxicology screens.
Some nitazenes could be hundreds to thousands of times more potent than morphine and in some cases 10 to 40 times stronger than fentanyl. [2]
The Rise of Nitazenes
Recent statistics indicate a troubling increase in the presence of Nitazenes, with reports of overdoses and deaths attributed to these compounds climbing sharply. The emergence of Nitazenes on the drug market can be attributed to several factors:
- Advances in chemical synthesis and the accessibility of precursor chemicals have made it easier for illicit drug manufacturers to produce these potent opioids and evade law enforcement.
- The ongoing demand for stronger and more addictive substances drives the diversification of the drug supply, as users develop tolerance to existing opioids like fentanyl.
The allure of Nitazenes for drug traffickers lies in their potency with no increase in volume, which exceeds that of fentanyl, making them attractive for those looking to maximize the strength of their products with minimal volume.
Additionally, the legal ambiguity surrounding many new synthetic opioids complicates law enforcement efforts to curb their distribution. As they are not always explicitly controlled substances in every jurisdiction, manufacturers exploit these legal loopholes to distribute Nitazenes widely before regulatory action can catch up.
The emergence of Nitazenes represents a significant escalation in the opioid epidemic, posing profound challenges for public health, law enforcement, and drug policy. Their potency makes them extremely dangerous, as even small amounts can lead to overdose and death.
The rise of Nitazenes on the street drug scene underscores the need for comprehensive strategies to address the evolving nature of drug abuse and addiction, focusing on prevention, education, and the development of effective treatments for substance use disorders.
The Dangers of Nitazenes
The emergence of Nitazenes as a potent class of synthetic opioids has escalated the already dire opioid crisis, introducing new risks and challenges. Nitazenes, often significantly more potent than fentanyl, which is already up to 50 times stronger than heroin, represent an unprecedented threat in the landscape of substance abuse.
The potency of Nitazenes varies significantly among different compounds within the Nitazene class. This extreme potency greatly increases the risk of overdose, as users may not be aware of the strength of the substances they are consuming, especially when Nitazenes are mixed with other drugs or misrepresented as less potent opioids.
One report stated that “Nitazenes are available in powders, counterfeit tablets, or liquids and may be mixed with inert substances and/or combined with other drugs, such as heroin, fentanyl, and benzodiazepines’ [2]. Many overdose victims have no idea they are ingesting these dangerous and extremely potent drugs.
Overdose risks associated with Nitazenes are alarmingly high, due in part to their high affinity for mu-opioid receptors in the brain. Overdoses can lead to a rapid onset of life-threatening symptoms, including:
- Respiratory depression, where breathing becomes shallow or stops altogether, leading to hypoxia and, potentially, death, is now classed in these types of cases as “toxic brain injury”.
- Pinpoint pupils.
- Unconsciousness.
- Blue-colored lips or nails due to oxygen deprivation.
The risk of overdose is compounded by the variability in potency among different Nitazenes and the possibility of encountering them in combination with other substances, which can unpredictably amplify their effects.
Long-Term Health Impacts
Nitazenes are not widely researched or discussed, even by authoritative agencies. The long-term health impacts of Nitazenes are still being understood, but the known effects are concerning. Regular use of potent opioids can lead to a range of adverse health outcomes, including but not limited to:
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Gastrointestinal issues.
- Immune system suppression.
- Toxic brain injury.
The risk of developing persistent opioid use disorder is significant, as the body’s tolerance to the drug’s effects can lead to physical dependence. Withdrawal symptoms can be severe, including pain, insomnia, diarrhea, vomiting, and intense cravings, making it extremely difficult for individuals to cease use without medical assistance.
Beyond the physical health impacts, the psychological toll of Nitazene addiction can be devastating. Opioid addiction can lead to significant changes in the brain, affecting mood, decision-making, and the ability to experience pleasure. This can exacerbate existing mental health issues or lead to new ones, including depression and anxiety disorders.
The cycle of addiction—chasing the drug’s euphoric effects, experiencing withdrawal, and then using it again to alleviate discomfort—can trap individuals in a destructive pattern that is challenging to break.
The social consequences of Nitazene use are also profound. Addiction can:
- Strain relationships.
- Lead to job loss.
- Financial instability.
- Increased criminal activity related to drug seeking and use.
The fabric of communities can be eroded as more individuals fall into the cycle of addiction, leading to increased healthcare costs, law enforcement burdens, and a loss of productive members of society.
In summary, the dangers of Nitazenes extend far beyond their immediate risk of overdose. The long-term health impacts, psychological toll, and broader social consequences highlight the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to address this emerging threat.
Critical components of a multi-faceted response to the Nitazene crisis include:
- Family education for teens.
- School education on the risks of synthetic opioids.
- Public health interventions.
- Enhanced treatment options for addiction.
- Robust law enforcement efforts to curb the supply of these dangerous drugs.

How Nitazenes Are Entering Teen Lives
The introduction of Nitazenes into the illicit drug market has not only escalated the opioid crisis but also posed a significant risk to teenagers, a demographic particularly vulnerable to the allure and dangers of substance use.
The psychological toll and risk of addiction associated with Nitazene use are profound, exacerbated by the ways these substances are infiltrating teen lives. The mechanisms of accessibility, the influence of social media, legal loopholes, and misconceptions about safety contribute to the growing concern among health professionals, parents, and educators alike.
Accessibility and Social Media Influence
Nitazenes, with their potent effects, are increasingly finding their way into the hands of teenagers, facilitated by their accessibility through both traditional drug trafficking channels and, more insidiously, through social media platforms.
Social media has become a double-edged sword; while it connects us, it also serves as a conduit for the proliferation of drug culture among teens. Dealers use social media to market their products, often disguising the true nature of these substances or promoting them under the guise of being ‘safer’ alternatives to other opioids. The anonymity and broad reach of the internet allow dealers to target vulnerable populations, including teenagers, who may be drawn to the idea of experimenting with substances without fully understanding the risks involved.
The allure of Nitazenes is further magnified by the way they are presented online, often accompanied by misinformation about their effects and safety. Peer pressure, the desire for social acceptance, and the influence of drug use depicted as glamorous or risk-free on social media can lead teens to underestimate the dangers of these potent opioids.
The Veil of Legality: A Dangerous Gray Area for Teens
One of the most insidious aspects of the Nitazene threat is the veil of legality that surrounds these substances. Due to the slow pace of legal systems in categorizing and controlling new synthetic drugs, Nitazenes often exist in a gray area of legality. This lag allows them to proliferate more freely before authorities can crack down on their distribution. The perception that a substance is ‘legal’ or not yet classified as illegal can create a dangerous misconception among teens that these drugs are safe or at least safer than their illicit counterparts.
This legal ambiguity is exploited by manufacturers and dealers who market Nitazenes as legal highs, further complicating efforts to educate teens about the risks. The notion that something legal is inherently safer is a profound misunderstanding, particularly when it comes to synthetic opioids, which can be far more potent and unpredictable than naturally occurring substances.
The Devastating Effects of Nitazenes on Teens
The psychological and physical effects of Nitazenes on teenagers can be devastating. At a critical stage of brain development, teens are particularly susceptible to the addictive properties of opioids. The high potency of Nitazenes means that even experimental use can quickly lead to dependence, with withdrawal symptoms making cessation extremely difficult without professional help.
Beyond the risk of addiction, the use of Nitazenes can have severe psychological impacts. These can include exacerbating or triggering mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis. The social consequences of drug use, such as:
- Isolation from peers and family
- Declining academic performance
- Involvement in criminal activities
Drug addiction can further compound these psychological effects, creating a cycle of use and dependency that is difficult to break.
Moreover, the stigma associated with drug addiction can prevent teens from seeking the help they need, for fear of judgment or punishment. This stigma, coupled with a lack of awareness about the true nature of Nitazenes, leaves many teens—and their families—ill-prepared to deal with the consequences of use.
If you’re concerned that your teen might be experimenting with substances such as fentanyl or heroin, it’s crucial to understand that drug dealers often lace these drugs with Nitazenes to boost their potency and profits. Our teen opioid treatment program has successfully guided numerous Texas teens toward recovery. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us for support.
Summary
The infiltration of Nitazenes into the lives of teenagers is a complex problem, rooted in the:
- Accessibility of these drugs
- The influential role of social media
- Legal loopholes
- Widespread misconceptions about their safety
The psychological toll and risk of addiction are significant, with long-lasting effects on the health, well-being, and prospects of young individuals. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach, including education, regulation, and support for those affected. Communities must come together to:
- Raise awareness about the dangers of Nitazenes.
- Support legislation that closes legal loopholes.
- Provide resources for teens struggling with substance use.
- Ensure they have access to the help they need to overcome the challenges posed by these potent drugs.
States Most Affected by Nitazenes
First identified around 2019 in the Midwest, this dangerous drug has moved into Colorado, the Southern states, and, more recently, along the Eastern seaboard and Washington D.C. and the Tri-State area. In 2022, two deaths were reported in the Houston area.
As Nitazenes emerge as a significant threat in the opioid crisis, certain states in the U.S. have been more affected than others, witnessing alarming trends in usage, overdoses, and challenges in law enforcement. These synthetic opioids, more potent than fentanyl, have contributed to a spike in overdose deaths and presented new obstacles in the battle against drug abuse.
Recent statistics and reports indicate that states such as Ohio, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania are among those most severely impacted by Nitazenes. These areas, already grappling with high rates of opioid addiction and overdose deaths, have reported a concerning rise in incidents linked to Nitazenes.
Ohio, for example, has seen a significant number of overdose deaths attributed to these drugs, with public health officials sounding the alarm on their potency and the difficulty in reversing overdoses even with naloxone, a medication used to block the effects of opioids in emergencies.
West Virginia, which has the highest opioid overdose death rate in the nation, has also reported an uptick in Nitazene-related incidents. The state’s struggles with opioid addiction are compounded by the introduction of Nitazenes, which are often mixed with other substances, making them more dangerous and overdose treatments less effective.
Pennsylvania has experienced similar challenges, with law enforcement and public health officials noting an increase in Nitazene presence on the streets. These drugs have been found in combination with heroin and fentanyl, contributing to a rise in overdose deaths across the state.
States’ Legal Response
In response to the growing threat posed by Nitazenes, states have implemented various measures aimed at curbing their distribution and use. Public health initiatives have focused on increasing awareness about the dangers of these substances, expanding access to naloxone, and enhancing substance use disorder treatment options. For instance, Ohio has launched educational campaigns targeting both the public and healthcare professionals, emphasizing the need for vigilance and the availability of treatment resources.
Legal measures have also been a critical component of state-level responses. Several states have moved to classify Nitazenes as controlled substances, making their possession, distribution, and manufacture illegal. This legal action aims to give law enforcement the tools needed to combat the distribution of Nitazenes more effectively.
Moreover, states are collaborating with federal agencies to track the distribution patterns of Nitazenes and intercept shipments, aiming to cut off the supply at its source. These efforts are complemented by initiatives to support individuals struggling with addiction, including expanding access to rehabilitation services and supporting recovery programs.
The challenge posed by Nitazenes is complex and urgent, requiring a coordinated response that addresses both the supply of these dangerous drugs and the demand driven by addiction. State-level initiatives, while crucial, underscore the need for a comprehensive national strategy to combat the evolving opioid crisis effectively.

Tips for Starting Discussions About Drug Use
Begin conversations about drugs and their dangers early in your child’s life and continue these discussions regularly.
Educate Yourself
Understand the facts about Nitazenes and other opioids to provide accurate information.
Create a Safe Space
Encourage open dialogue where your teen feels safe to share their thoughts and questions without judgment.
Listen More Than You Speak
Foster an environment of trust by listening attentively to your teen’s concerns and experiences.
Importance of Maintaining an Open Line of Communication
Maintaining an open line of communication helps build trust and facilitates a supportive relationship. It allows parents to guide their teens through the complexities of drug information and misinformation, especially with the prevalence of social media.
Recognize Warning Signs: Behavioral and Physical Signs of Opioid Use
Behavioral Changes
Look for shifts in mood, withdrawal from family and social activities, changes in friend groups, or decreased interest in hobbies.
Physical Signs
Noticeable signs may include changes in sleeping patterns, unexplained weight loss, poor hygiene, or the appearance of new, unexplained injuries or marks.
When to Seek Help
If you observe a combination of these signs and suspect opioid use, it’s crucial to seek help immediately. Contact a healthcare professional, a counselor, or a local addiction support group to discuss the best course of action.
Preventative Measures to Keep Teens Safe
Education
Inform your teen about the dangers of drug use, emphasizing the risks of potent opioids like Nitazenes.
Set Clear Expectations
Discuss your family’s expectations regarding drug use and the consequences of violating those expectations.
Encourage Healthy Activities
Promote involvement in sports, hobbies, or other engaging activities that provide natural highs and a sense of community.
Resources for Intervention and Support
Professional Help
Consider seeking advice from addiction specialists or therapists who have experience with teen drug use.
Support Groups
Look into support groups for families and teens dealing with substance abuse, such as Narcotics Anonymous or local community resources.
Educational Programs
Engage in school or community programs designed to prevent drug use, offering a comprehensive approach to education and prevention.
By adopting a comprehensive strategy that includes open conversations, recognizing warning signs, and employing prevention and intervention tactics, parents can play a crucial role in safeguarding their teens against the dangers of Nitazenes and other opioids. This proactive approach is essential in navigating the challenges of adolescence in today’s complex world.
Navigating the Legal Landscape
Navigating the legal landscape surrounding Nitazenes, a potent class of synthetic opioids, presents a complex challenge as communities, legislators, and law enforcement grapple with an evolving drug crisis. The regulatory framework for Nitazenes is under constant scrutiny as authorities seek to adapt to the threats posed by these substances.
Current Legislation on Nitazenes
The laws regulating Nitazenes are an amalgamation of federal and state statutes designed to control their distribution, manufacture, and possession. At the federal level, Nitazenes are often classified under analog acts, intended to cover synthetic substances similar to already controlled substances.
However, the rapid innovation in synthetic opioid manufacturing often outpaces the existing regulatory frameworks, leading to a lag in effective legal control. Recognizing this, legislation is evolving, with efforts to streamline the process for classifying new synthetic opioids as controlled substances more swiftly.
Legislation is Changing in Response to the Crisis
In response to the crisis, there’s a push for more dynamic legislative tools that can quickly adapt to the introduction of new synthetic drugs like Nitazenes. This includes proposals for blanket legislation covering broader categories of synthetic opioids and enhancing the penalties for trafficking and distribution. Furthermore, there’s a significant emphasis on improving the tracking and monitoring of prescription medications to prevent diversion and misuse.
Ways Parents Can Advocate for Stricter Regulations
Parents play a crucial role in advocating for stricter regulations on Nitazenes. They can engage in lobbying efforts, participate in public comment periods for new regulations, and support organizations that push for policy changes. Joining or forming coalitions can amplify their voices, making their advocacy efforts more impactful.
The Importance of Community Education and Support
Community education and support are indispensable in the fight against Nitazenes. Informing the public about the dangers of these drugs, recognizing the signs of abuse, and understanding the legal implications are vital components of a comprehensive approach to mitigation.
Community support networks can offer essential resources for those affected, providing a pathway to recovery and rehabilitation. Through education and support, communities can foster a more informed and resilient environment, better equipped to tackle the challenges posed by Nitazenes and other synthetic opioids.
Key Takeaways
- Nitazenes are a new class of opioids often much more potent than Fentanyl, posing a significant overdose risk.
- Even though nitazenes have been identified in the illicit recreational drug supply, few clinicians are aware of them or their implications for emergency medicine.
- The emergence of Nitazenes represents a significant escalation in the opioid epidemic, posing profound challenges for public health, law enforcement, and drug policy.
- Overdose risks associated with Nitazenes are alarmingly high. Overdoses can lead to a rapid onset of life-threatening symptoms.
- Accessibility through legal loopholes and social media increases the risk of teen exposure.
- The psychological and physical effects of Nitazenes on teenagers can be devastating.
- First identified around 2019 in the Midwest, this dangerous drug has moved into Colorado, the Southern states, and, more recently, along the Eastern seaboard and Washington D.C. and the TriState area.
- By adopting a comprehensive strategy that includes open conversations, recognizing warning signs, and employing prevention and intervention tactics, parents can play a crucial role in safeguarding their teens.
- Navigating the legal landscape surrounding Nitazenes, a potent class of synthetic opioids, presents a complex challenge as communities, legislators, and law enforcement grapple with an evolving drug crisis.
Sources
[1] Understanding the Opioid Overdose Epidemic. 2023. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
[2] Pergolizzi Jr J, Raffa R, LeQuang J K, et al. (June 21, 2023) Old Drugs and New Challenges: A Narrative Review of Nitazenes. Cureus 15(6): e40736. doi:10.7759/cureus.40736
Hypoxia. 2022. Cleveland Clinic.
Illicit Drug Trends and Emerging Threats in the Houston HIDTA, StopDrugsHouston.org

Anna graduated from Texas Tech University in 2012 with a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology and from Texas Wesleyan University in 2015 with a Master of Arts in Professional Counseling. Anna has been in the mental health field since 2015 and held a variety of leadership roles since 2017 in Residential, Inpatient, PHP/IOP and private practice levels of care. Anna approaches therapy and leadership with the mindset that we are all one life event from seeking care ourselves and aims to foster an environment in which both the client and staff well-being are the priority. Anna is an introverted foodie who enjoys reading, watching dateline/sports and spending time with her husband, daughter, and fur babies, Dora & Teddy.